Introdcution
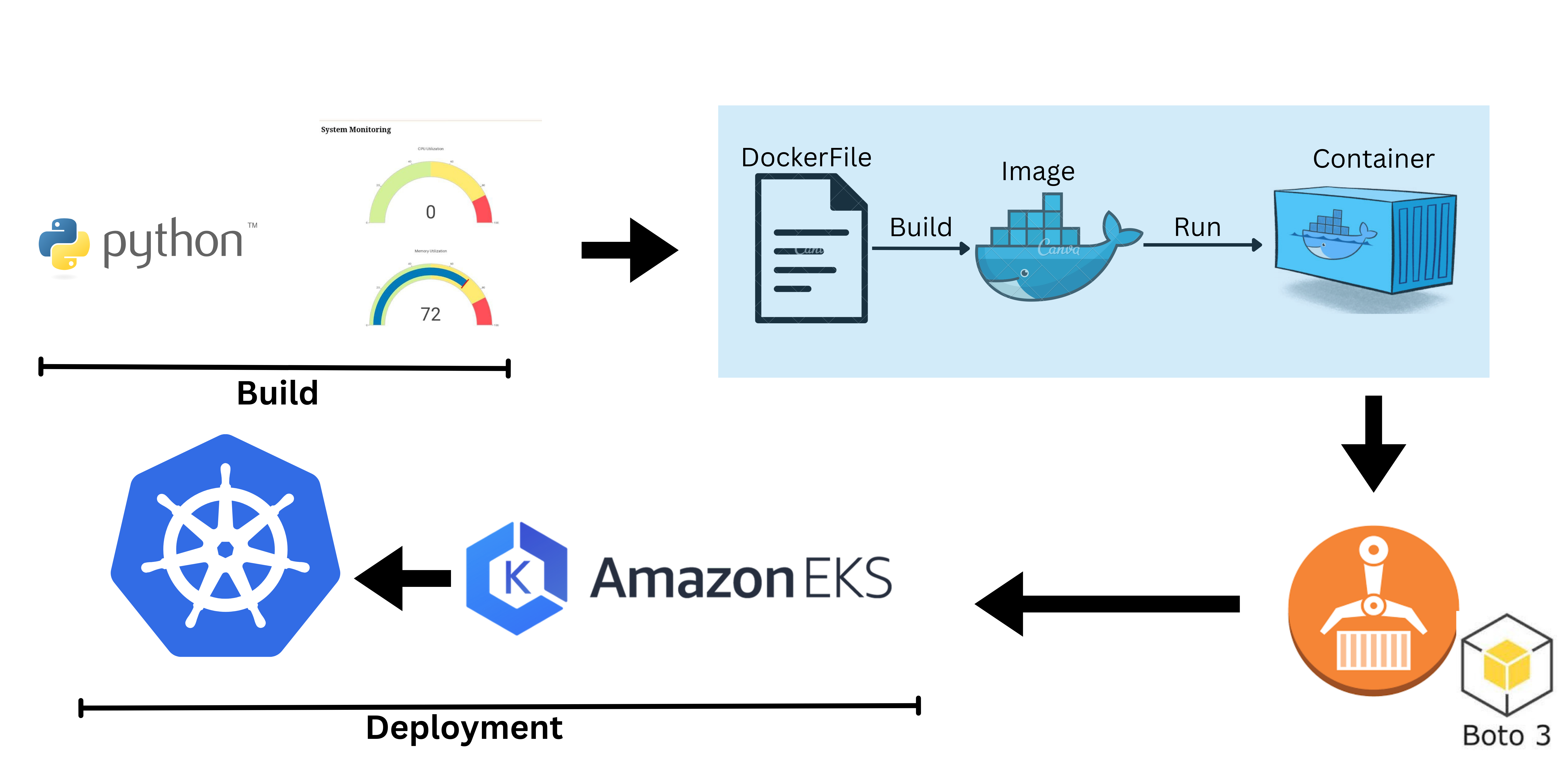
A Python monitoring application utilizing Flask and psutil, providing invaluable insights into system performance. The application's Docker image is crafted through a Dockerfile, and leveraging the Boto3 module, this image is securely pushed to the Elastic Container Registry (ECR) repository. The deployment of this application on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is achieved through a Python script, utilizing an EKS cluster and nodegroups for efficient orchestration.
Technical Stack:
- Part 1: Deploying the Flask application locally
- Step 1: Clone the code: Clone the code from the repository
- Step 2: Install dependencies: The application uses the psutil and Flask, Plotly, boto3 libraries. Install them using pip
- Step 3: Run the applicationTo run the application, navigate to the root directory of the project and execute the following command:
python3 app.py
- Part 2: Dockerizing the Flask application
- Step 1: Create a Dockerfile: Create a Dockerfile in the root directory for app.py
- Step 2: Build the Docker image:To build the Docker image, execute the following command:
docker run -p 5000:5000 - Step 3: Run the Docker container
- Part 3: Pushing the Docker image to ECR
- Step 1: Create an ECR repository: Create an ECR repository using ecr.py
- Step 2: Push the Docker image to ECR : Push the Docker image to ECR using the push commands on the console:
docker push:
- Part 4: Creating an EKS cluster and deploying the app using Python
- Step 1: Create an EKS cluster: Create an EKS cluster and add node group
- Step 2: Create a node group: Create a node group in the EKS cluster.
- Step 3: Create deployment and service Once you run this file by running “python3 eks.py” deployment and service will be created.
Check by running following commands:
kubectl get deployment -n default (check deployments)
kubectl get service -n default (check service)
kubectl get pods -n default (to check the pods)